
European eel
Anguilla anguilla
There are some 32 native fish species in Catalonia that live, at least some of their lives in fresh water. There are also at least 25 non-native or allochthonous species that are well-established here. The dominant species vary along the course of the river. In the same river basin different fish will be found living in specific areas that are defined by their environmental requirements: temperature, the speed of the river, the type of substrate, etc.
Many native fish are in regression and in a fragile state of existence. All are affected, in one way or another, by problems related to the over-use of water, poor connectivity and competition with invasive species.
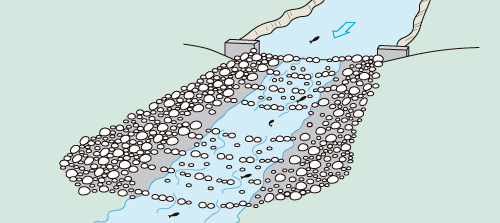
The movements of fish are affected by water shortages, pollution, and hydraulic structures, such as dams, locks, fords, walkways, irrigation pumps, etc.
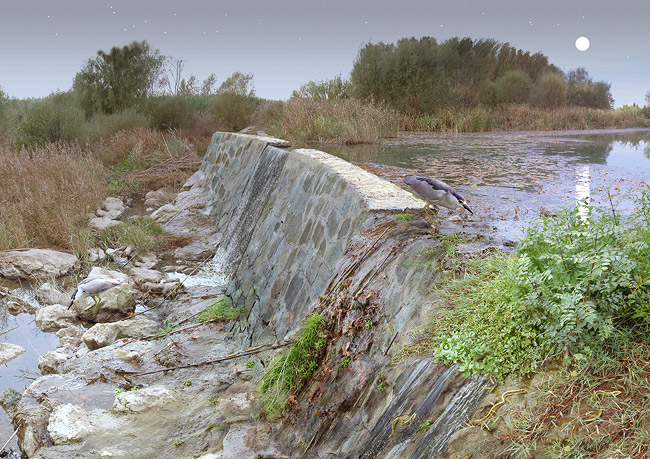

A weir preventing fish migration. Illustration by Toni Llobet at Ordeix i Bretxa (2007).
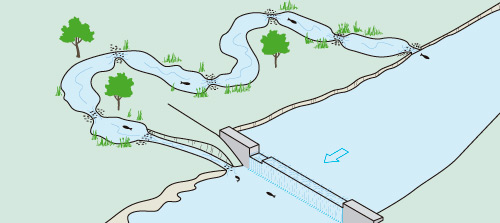
In order to improve connectivity for fish in rivers, ponds and wetlands, one option is to either totally or partially remove the obstacles in their path, or if this is not viable, then constructing special devices to aid fish as they travel up and downstream is an alternative.
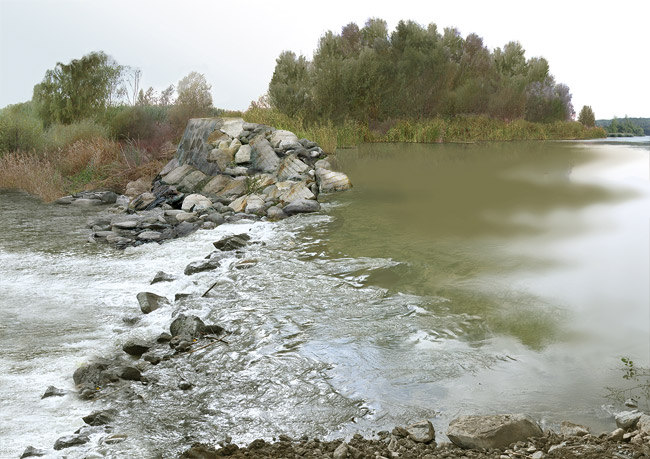

The destruction of a river barrier to facilitate the movement of fish.
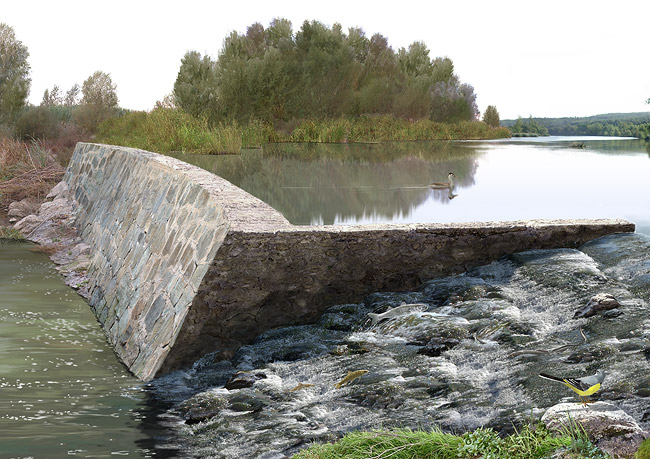

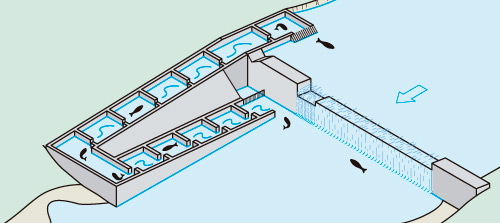
A fish ramp at a weir. Illustration by Toni Llobet at Ordeix i Bretxa (2007).
There are many different devices for aiding the movement of fish. Some are more natural by design (fish ramps and lateral river by-passes) and are generally more efficient, while others are more technical in design and that require more complex maintenance (pool passes, fish lifts and fish locks, among others).
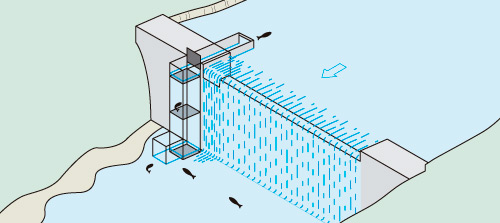
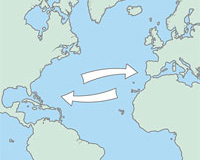
The eel is the only catadromous fish in this country. It spends most of its life in rivers, ponds or wetlands, in fresh or salt water environments, it only returns to the sea, and then to the Atlantic Ocean, to reproduce. It swims thousands of kilometers. This fish would today be thriving in many rivers if it were not for over-fishing and the barrier effect of dams and locks.

European eel
Anguilla anguilla
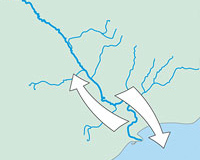
Anadromous fish spend most of their lives in the sea, where they grow, before returning to continental waters to spawn and reproduce.
Allis shad
Alosa alosa
Twaite shad
Alosa fallax
European sturgeon
Acipenser sturio
Sea lamprey
Petromyson marinus
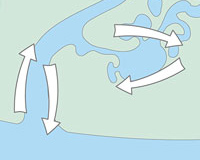
Amphidromous fish (although this classification is somewhat controversial and, in general, are also considered catadromous) move between the sea, where they usually breed, and rivers and marshes, where they go to feed.
Thinlip mullet
Liza ramada
Thicklip grey mullet
Chelon labrosus
Striped mullet
Mugil cephalus
Big-scale sand smelt
Atherina boyeri
European flounder
Platichthys flesus
Black-striped pipefish
Sygnathus abaster
Golden grey mullet
Liza aurata
Leaping mullet
Liza saliens
European bass
Dicentrarchus labrax
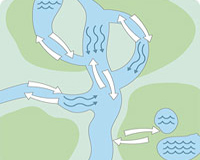
Potamodromous fish migrate, especially in order to reproduce. They swim upstream or into flooded river banks to spawn, while looking for the best places for their eggs and their newly-born offspring: in streams, ponds or marshes, whether permanent or temporary.
Mediterranean barbel
Barbus meridionalis
Catalan barbel
Barbus haasi
Ebro barbel
Luciobarbus graellsii
Catalan chub
Squalius laietanus
Iberian chub
Squalius pyrenaicus
Bermejuela
Achondrostoma arcasii
Ebro nase
Pseudochondrostoma miegii
Freshwater blenny
Salaria fluviatilis
European bullhead
Cottus gobio
Western three-spined stickleback
Gasterosteus gymnurus
Brown trout
Salmo trutta
Iberian loach
Cobitis paludica
Spanish toothcarp
Aphanius iberus
Valencia toothcarp
Valencia hispanica
Many exotic fish species that were once owned as pets have been released and they now live in local rivers. These fish are a serious issue for autochthonous species as, among other reasons, they are highly competitive and easily replace native species at risk of extinction. Invasive species need to be controlled and we need to ensure that more fish of this type are not introduced.
Common rudd
Scardinius erythrophthalmus
Stone loach
Barbatula barbatula
Black bullhead
Ameiurus melas
Stone moroko
Pseudorasbora parva
Eastern mosquitofish
Gambusia holbrooki
Pumpkinseed
Lepomis gibbosus
European perch
Perca fluviatilis
Rainbow trout
Oncorhynchus mykiss
Northern pike
Esox lucius
Common bleak
Alburnus alburnus
Goldfish
Carassius auratus
Common carp
Cyprinus carpio
Iberian gudgeon
Gobio lozanoi
Adour minnow
Phoxinus bigerri
Common roach
Rutilus rutilus
Wels catfish
Silurus glanis
Zander
Sander lucioperca
Brook trout
Salvelinus fontinalis
Tench
Tinca tinca
Largemouth bass
Micropterus salmoides
Illustrations: © Toni Llobet